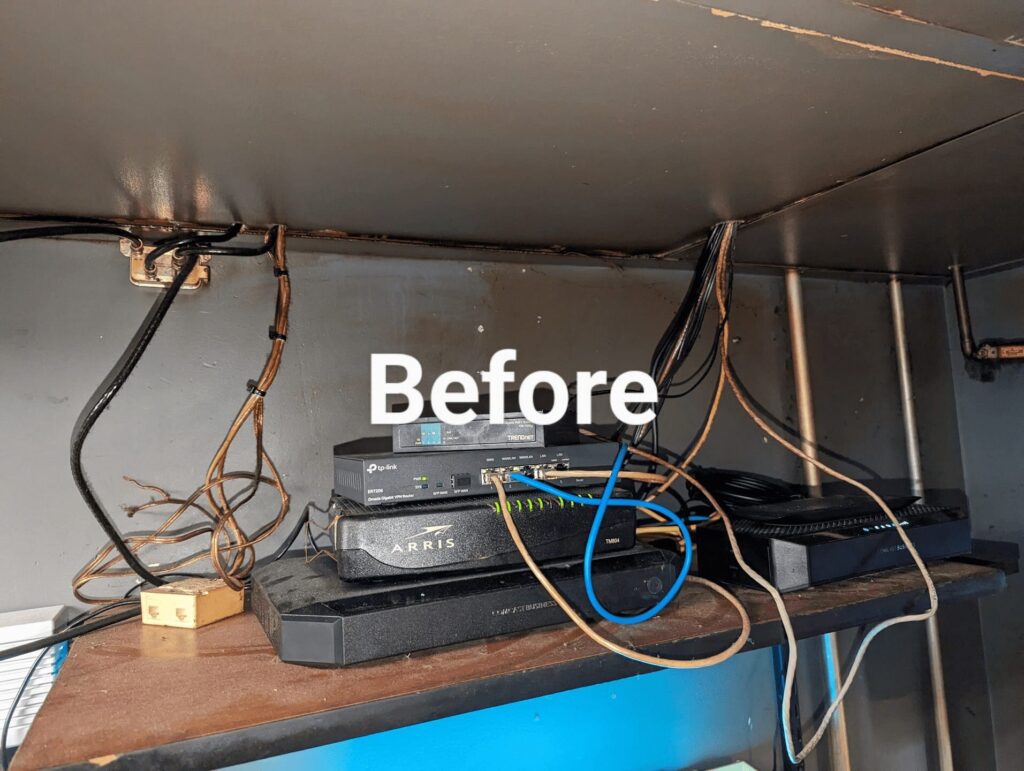
Make a file called “scriptmailssl.sh” and open the nano file editor. Paste these codes and save it!
#!/bin/bash
# This script takes the certs generated by Nginx Proxy Manager
# and copies it to the mailcow docker container.
# Before use, make sure you update the path to your docker data and locate which cert belongs to mailcow
cp /home/applegater/docker/nginx/letsencrypt/live/npm-7/fullchain.pem /home/applegater/docker/mailu/mailcow-dockerized/data/assets/ssl/my.richardapplegate.io/cert.pem
cp /home/applegater/docker/nginx/letsencrypt/live/npm-7/privkey.pem /home/applegater/docker/mailu/mailcow-dockerized/data/assets/ssl/my.richardapplegate.io/key.pem
postfix_c=$(docker ps -qaf name=postfix-mailcow)
dovecot_c=$(docker ps -qaf name=dovecot-mailcow)
nginx_c=$(docker ps -qaf name=nginx-mailcow)
docker restart ${postfix_c} ${dovecot_c} ${nginx_c}chmod +x /home/applegater/docker/scriptmailssl.sh
Add a cronjob every month.
crontab -e 0 1 * */2 * bash /home/applegater/docker/scriptmailssl.sh >/dev/null 2>&1It’s going to do the job for you every month.